Collagen & Elastin: How These Proteins Affect Skin Aging
These vital skin components start to diminish with age and sun damage — here's what you can do about it.
Published:
5 minute read
Anyone concerned about skin aging has heard of collagen and elastin — but most people don’t really know what they are, how they work, or why we lose them over time. These proteins play a major role in keeping skin looking firm, smooth and resilient, yet they naturally change as we get older.
So what exactly are collagen and elastin, and how do they influence visible aging? According to Sandra Lee, MD (aka Dr. Pimple Popper), understanding these proteins is the first step toward taking better care of your skin.
Fast Facts: Collagen and elastin
- Collagen gives skin its structure
- Elastin helps skin stay flexible
- Both decline due to age and lifestyle factors
- Healthy habits and good skincare help protect them
Article Quick Links
What is collagen?
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body, and it plays a major role in giving skin its strength and firmness. Within the dermis, collagen fibers create a supportive framework that keeps skin looking smooth, lifted and resilient.
There are sixteen different varieties of collagen in the human body, each made from slightly different combinations of amino acids. Type I collagen is the most common in skin and is responsible for its firm, structured appearance. Dr. Lee notes that in younger skin, collagen fibers are tightly organized and densely packed, which is why skin appears so plump and even.
As we age, collagen naturally becomes less abundant and less structured. This gradual decline contributes to fine lines, texture changes and a reduction in firmness over time.
What is elastin?
If collagen acts as the skin’s internal scaffolding, elastin is what makes that scaffolding flexible. Elastin is extremely stretchable — roughly one thousand times more flexible than collagen — allowing skin to move, bend and bounce back without losing its shape.
Elastin forms when multiple tropoelastin molecules link together to create spring-like fibers. Even though there is much less elastin in the skin compared to collagen, its role is essential for maintaining natural elasticity and smoothness. It’s also critical in organs like the lungs and large blood vessels.
“Once elastin fibers are damaged, the skin has a very limited ability to rebuild them," notes Dr. Lee. "That’s why protecting elastin is just as important as supporting collagen.”

What causes collagen and elastin loss?
Production of both proteins naturally slows as we age. But several factors can accelerate this process:
- Intrinsic aging: Collagen begins to decline in the mid-thirties at about one percent per year.
- Hormonal changes: After menopause, reduced estrogen leads to a more dramatic drop in collagen production.
- Sun exposure: UV radiation damages collagen and elastin structures and speeds up visible aging.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, alcohol use, chronic stress, poor sleep and low physical activity all contribute to breakdown within the dermis.
Dr. Pimple Popper's Collagen & Elastin Care
What happens when we lose collagen and elastin?
When collagen and elastin fibers weaken, the dermis becomes less organized, less flexible and more compact, with a gradual decline in natural hydration. Over time, these structural shifts start to appear on the surface as:
- Fine lines and wrinkles
- Sagging
- Crepiness
- Thinning skin
- Slower wound healing
“People often notice dullness or texture changes before wrinkles,” says Dr. Lee. “Those are early clues that the collagen-elastin network is shifting beneath the surface.”
How to boost collagen and elastin
There’s very limited evidence that collagen-enriched creams can directly increase collagen or elastin in the skin, since most collagen molecules are too large to penetrate the dermis. And while some recent research suggests hydrolyzed collagen supplements may help improve hydration or elasticity, results are mixed and not considered a primary strategy by dermatologists.
Instead, experts focus on habits and ingredients that support the skin’s natural ability to maintain and rebuild its own structure.
Controlled trauma
- Microneedling and fractional lasers create micro injuries that stimulate collagen and elastin production during healing.
- These treatments help strengthen the dermal matrix over time.
Topical skincare
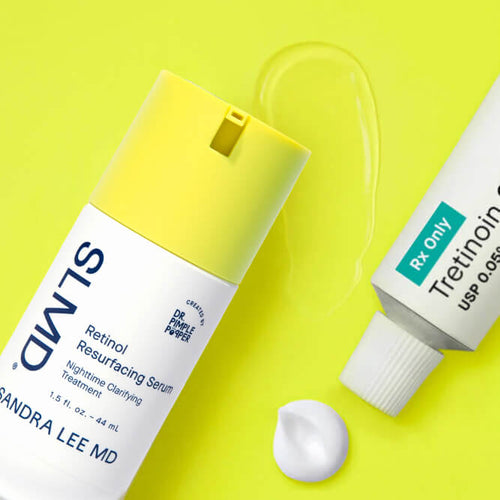
- Retinoids encourage collagen and elastin formation. Try: SLMD Retinol Resurfacing Serum.
- Vitamin C supports collagen synthesis and helps protect existing fibers from breakdown. Try: SLMD Vitamin C Serum.
- Sunscreen helps prevent UV-induced collagen and elastin damage. Try: SLMD Daily Moisturizer with SPF 15.
Nutrition and supplements
- The jury is still out on whether collagen supplements directly improve collagen or elastin levels.
- A nutrient-rich diet provides the amino acids and antioxidants needed to support healthy skin structure.
“Skincare can’t replace the collagen or elastin you’ve already lost, but it can improve the quality of the fibers you still have," says Dr. Lee. "And that’s where consistency makes a real difference.”
Common questions about collagen and elastin
Q: Can skincare products increase collagen and elastin?
A: They can’t replace what has already been lost, but ingredients like retinoids and vitamin C help support collagen and elastin production while reducing further breakdown.
Q: What damages collagen and elastin the most?
A: UV radiation is the biggest external factor. Smoking, stress and poor sleep also contribute to structural damage over time.
Q: When do collagen and elastin start to decline?
A: Collagen begins declining around the mid-thirties, while elastin production slows even earlier. Declines become more rapid during menopause due to reduced estrogen.
Q: Can collagen supplements improve skin firmness?
A: Research is mixed. Supplements don’t deliver collagen directly to the skin, but they may provide amino acids that support overall skin health.
Q: How can I protect my collagen and elastin long-term?
A: Daily sunscreen, antioxidants, retinoids and healthy lifestyle habits are the most effective ways to support these proteins.
Contributing sources:

Dr. Lee's Last Word
Collagen and elastin are essential proteins that keep our skin healthy and youthful, but we lose them with age and environmental damage. The key here is prevention: use sunscreen, retinol and antioxidants like vitamin C to avoid long-term damage.