Body Acne vs. Keratosis Pilaris: How to Tell the Difference & Treat Both
Dr. Pimple Popper helps decode these common body bumps — and offers tips on treatment & prevention.
Published:
4 minute read
Acne and keratosis pilaris (aka "strawberry" or “chicken" skin) are the most common types of body bumps — but how can you tell the difference? Though they may look similar, they have different causes and require different treatments. Dermatologist Sandra Lee, MD (aka Dr. Pimple Popper) explains how to identify each condition — and the best ways to treat them.
Article Quick Links

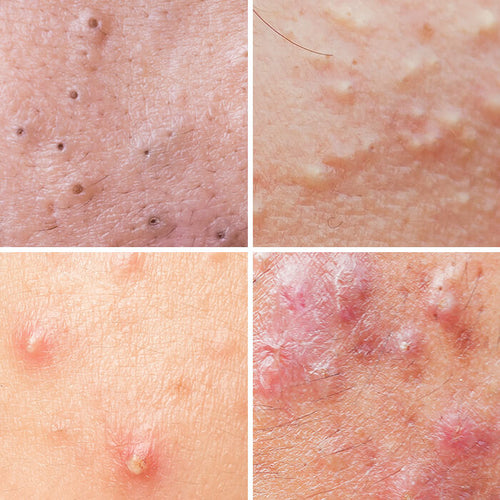
What does body acne look like?
Body acne can show up anywhere you have pores, but it’s most common on the back, chest, and shoulders. It comes in different forms:
-
Non-inflammatory acne ( blackheads and whiteheads)
-
Inflammatory acne ( papules, pustules, nodules, cysts)
Common characteristics of body acne:
- Found on oily to normal skin
- Small bumps that may be red, inflamed, or filled with pus
- Can appear in clusters or isolated spots
- Typically found on the back, chest, shoulders, and sometimes buttocks

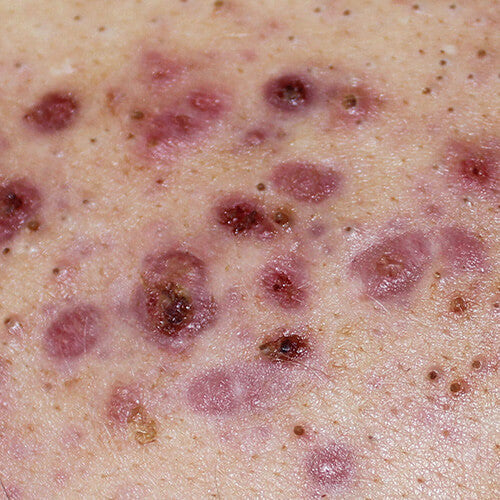
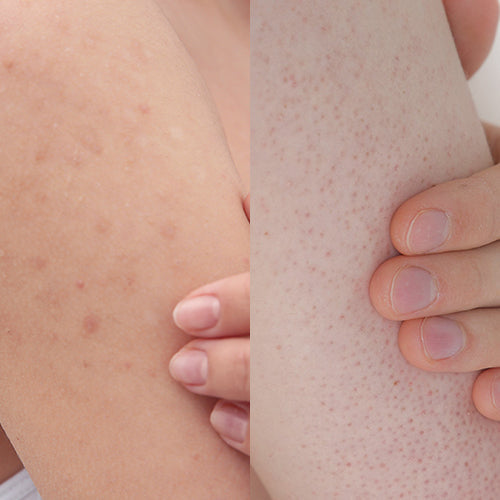
What does keratosis pilaris look like?
Keratosis pilaris (KP) is a buildup of keratin (a protective protein in the skin) that blocks hair follicles, forming rough, dry patches of tiny bumps. It’s often called “chicken skin” or “strawberry skin” due to its appearance.
Common characteristics of keratosis pilaris:
-
Dry, rough skin texture
- Small, sandpaper-like bumps (not inflamed or pus-filled)
- Found in patches rather than isolated breakouts
- Most common on the upper arms, thighs, buttocks, and cheeks
While KP isn't harmful, it can be persistent and often runs in families.
How to tell the difference between body acne and keratosis pilaris
| FEATURE | BODY ACNE | KERATOSIS PILARIS (KP) |
|
Cause |
Clogged pores from oil & dead skin cells | Buildup of keratin in hair follicles |
| Common locations | Back, chest, shoulders, buttocks | Upper arms, thighs, cheeks, buttocks |
| Appearance | Red or white bumps, sometimes pus-filled | Small, rough, dry bumps in patches |
| Skin type | Normal to oily | Dry to normal |
| Triggers | Sweat, friction, hormones, bacteria | Genetics, dry skin, buildup of dead skin |
| Treatment focus | Clearing clogged pores & reducing bacteria | Exfoliating & moisturizing |
Dr. Pimple Popper's Body Acne Picks
Best treatments for body acne
Because body acne is caused by excess oil and dead skin, the best approach is exfoliation and acne-fighting ingredients.
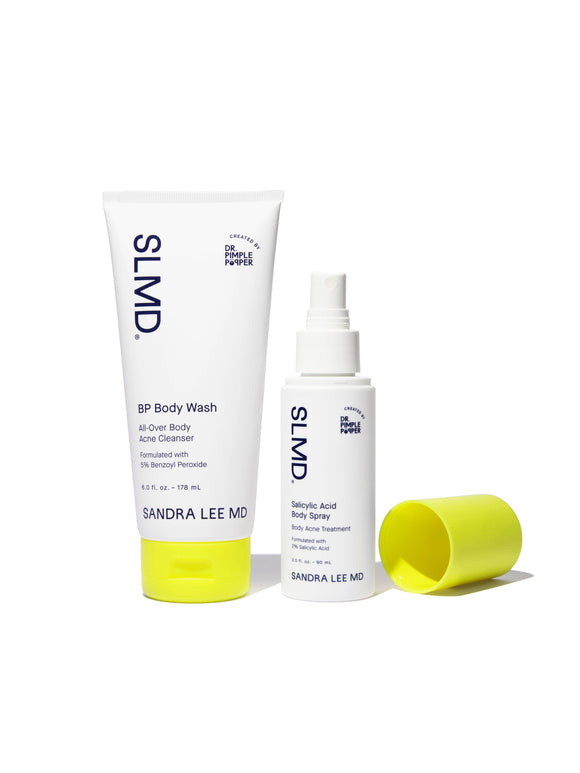
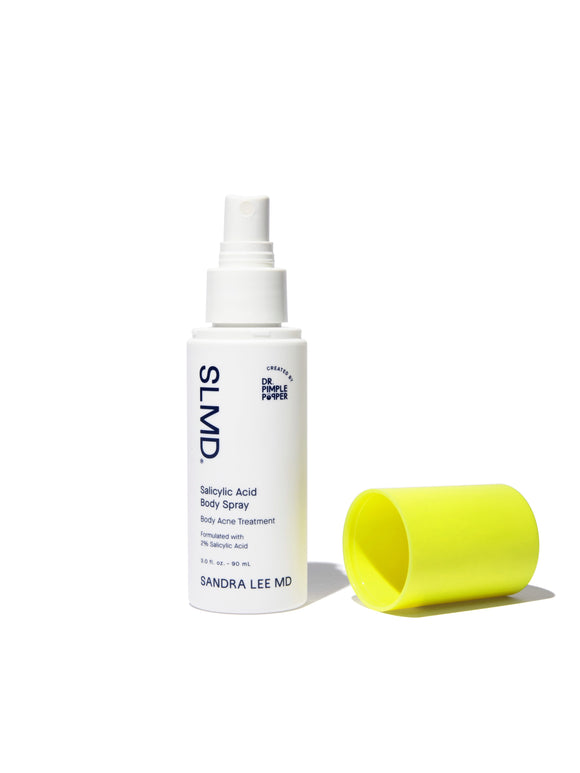
- Salicylic acid: a beta hydroxy acid (BHA) that penetrates deep into pores to clear out excess oil and dead cells. Try: SLMD Salicylic Acid Body Spray — perfect for treating hard-to-reach areas like the back.
- Benzoyl peroxide: a powerful antimicrobial ingredient that kills acne-causing bacteria and reduces inflammation. Try: SLMD BP Body Wash — fights breakouts without over-drying.
- Exfoliating & hydrating: prevent clogged pores with regular exfoliation while maintaining moisture balance. Try: SLMD AHA/BHA Swipes — combines glycolic and salicylic acids for gentle exfoliation.
Pro tip: Shower after sweating and wear breathable fabrics to minimize friction and bacteria buildup.
Best treatments for keratosis pilaris
Since KP is caused by excess keratin, the best treatment is exfoliation and hydration to smooth rough patches.
- Glycolic acid: An alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) that dissolves dead skin buildup and smooths rough patches. Try: SLMD Glycolic Acid Body Scrub — a dual-action physical & chemical exfoliant.
- Hydrating ingredients: Keeping skin moisturized helps prevent further keratin buildup. Try: SLMD Glycolic Acid Body Lotion — exfoliates while deeply hydrating.
Pro tip: Exfoliate gently and consistently — harsh scrubbing can worsen irritation.
FAQs: Managing body acne & KP
Q: Can I have both body acne and KP at the same time?
A: It’s not common. While both affect hair follicles, body acne is caused by oil and bacteria, whereas KP results from keratin buildup. Research suggests that people with KP may actually be less prone to acne. If you’re unsure, a dermatologist can help determine what’s going on.
Q: How often should I exfoliate for body acne or KP?
A: Start with two to three times a week, then adjust based on how your skin reacts. Salicylic acid helps clear clogged pores for acne, while glycolic acid smooths rough, bumpy KP — just don’t overdo it!
Q: Can diet affect body acne or KP?
A: Possibly. Some research links dairy and high-glycemic diets to acne, while anecdotal evidence suggests gluten, dairy, or nutrient deficiencies may worsen KP. Though KP is mostly genetic, keeping skin hydrated and moisturized can improve its appearance.
Q: What should I do if my body bumps aren't acne or keratosis pilaris?
A: If your skin bumps don't match the typical signs of acne or keratosis pilaris, they could be due to other conditions like folliculitis, eczema, or ingrown hairs. Consulting a dermatologist can provide an accurate diagnosis. For more information on distinguishing between various skin conditions, check out our detailed guide here.

Dr. Lee's Last Word
Body bumps aren’t always acne — sometimes, they’re caused by excess keratin instead of clogged pores. That’s why it’s so important to know the difference between acne and keratosis pilaris — so you can treat them correctly! If you’re dealing with breakouts, go for salicylic acid and benzoyl peroxide. For KP, exfoliation and moisture are key.